-
 December 15 2025
December 15 2025
AI Poisoning: The New Frontier of Black Hat SEO Threatening Your Brand’s AI Visibility
You would think that after decades of Google battling Black Hat SEO tactics, the fight for online visibility would finally be on equal footing.
But that’s not true! The game has simply moved to a new arena.
Today, Black Hat SEO operators are no longer just stuffing keywords or buying backlinks. They’re exploiting a far more powerful system: AI-driven search.
Weaknesses in Large Language Models allow attackers to poison their training data. The result? Responses that only cite sources Black Hats want to rank.
If you want to stay visible in AI searches, you must understand AI poisoning. This guide explains what it is, how it works in SEO, and practical ways to protect your brand against it.
What is AI Poisoning?
From an SEO perspective, AI data poisoning means manipulating the way an AI model responds to a query by modifying its training data. This is done by attackers who want the AI tool to offer biased outputs that provide either incorrect information or only cite content that attackers want to rank.
Training data is the critical foundation that helps AI search algorithms learn information and make sense of the world. When someone adds misleading content into the huge datasets used to train Large Language Models, it can distort how the model understands facts, brand identities, and how different ideas connect. This results in AI citing information from less reliable and inaccurate sources.
Why AI Poisoning Should Matter to SEO Professionals
When we talk about SEO today, AI poisoning attacks have become a much bigger concern. People aren’t just relying on traditional search engines to rank webpages. They’re turning to AI-generated responses to discover information and make decisions.
Research makes this shift pretty clear:
- Website Traffic is Dropping:
A recent Bain & Company study found that about 60% of searches end right on the results page because users get the answers they need without clicking through to another site.
- AI Searches are Increasing:
More and more people are relying on AI platforms to satisfy their search queries. According to a report by Search Engine Land, AI search traffic increased by 527% in just 5 months between January and May 2025. We’re also seeing a strong generational shift. A report by Commerce shows that 1 in 3 Gen Z and 1 in 4 Millennials now prefer using AI platforms over other methods.
- Trust in AI is Rising Fast:
According to the 2025 State of Search report by Claneo, 79% of Americans trust AI search engines, and 77% trust AI chatbots for searches. Another report by Yext shows that 62% of global consumers trust AI tools to find new brands.

These studies show that generative AI data poisoning for black hat SEO can seriously affect your AI visibility. It can also expose a massive number of people to unreliable and even dangerous information online.
The Rise of Black Hat SEO: Old Tactics, New Technology
Let’s take a step back and look at how black hat SEO has evolved over the years. In the early days of search engines, people used to rely on black hat SEO techniques to rank for organic searches. They would hide white text on white backgrounds, build massive link farms full of low-quality backlinks, and stuff pages with so many keywords that the content barely made sense. These tricks worked because search algorithms were simple and easy to fool.
However, things changed when Google released its two major updates. Panda cracked down on thin content and keyword stuffing. Meanwhile, Penguin helps tackle manipulative link-building schemes. Then came more advanced, machine-learning-driven updates that tightened the screws even further.
Suddenly, the same tactics that once guaranteed top rankings led to harsh penalties and even complete removal from search results. By the mid-2010s, most experienced SEO professionals realized the game had changed for good.
The AI Era: A New Playground for Bad Actors
Modern AI systems are incredibly powerful, yet they share a critical weakness with those early search engines. They trust the data they’re trained on. Just as search engines once assumed websites were honest, Large Language Models think their training data is clean and reliable.
This is where things get interesting. Classic black hat SEO tactics now have modern counterparts in AI platform poisoning. They introduce malicious documents to poison the AI system’s training data and interfere with rankings. Some black hat SEO examples for AI models include:
- Content cloaking has turned into a subtle manipulation of training datasets.
- Link farms have become clusters of poisoned documents that appear naturally distributed across datasets.
- Keyword stuffing has changed into the use of specific trigger phrases that activate prompt-specific model behaviors.

Poisoning AI Models is Way Easier
Perhaps more concerning is that AI systems are even easier to manipulate. One recent research found that attackers need only about 250 malicious documents to meaningfully poison an AI model. It doesn’t even matter how large the overall dataset is.
Moreover, an analysis by VPNRanks shows that attackers need less than 7-8% manipulated data for accurate poisoning attacks. This is a dramatic shift. It’s a low barrier to entry and a clear warning that today’s AI systems face risks just like the easily manipulated days of online search engines.
Black Hat vs White Hat SEO in the Age of AI
Even with all the changes brought by AI, the core difference between black hat and white hat SEO hasn’t really changed. Black hat SEO means manipulating AI systems by introducing biased or misleading information into their training data. White hat SEO, on the other hand, focuses on producing value-driven content optimized for how AI models are naturally designed to learn and rank information.
The Temptation of AI Manipulation
Because AI systems are still developing and vulnerable, it’s easy for marketers to convince themselves that poisoning training data is just “getting ahead.” It’s the same way early black hat tactics once felt like clever tricks before Google began to penalize them. You might think, Why spend months building authority when it seems possible to influence AI responses in just a few weeks?
But history shows how unreliable that mindset is. AI platforms are regularly releasing major algorithm updates. And it’s only a matter of time for sites built on black hat tactics to collapse overnight. As defenses against AI poisoning will improve, those who tried to manipulate the models may end up blacklisted from training datasets. This will not only damage their brand reputation but may even lead to legal consequences.
The White Hat Alternative
Why use unethical means when there’s a safer and more sustainable path to dominate AI searches? With White Hat SEO, you can not only avoid penalties but also build a lasting brand authority that both search engines and AI chatbots will trust.
Here’s what you can do:
- Create factual and original content that AI models naturally want to reference.
- Strengthen your brand across multiple platforms so your legitimate work becomes dominant in training datasets.
- Make your content easy for AI to understand with clear structure, accurate details, and conversational explanations.
- Show expertise with high-value material that genuinely helps your audience.
This is the kind of content AI systems are designed to cite in their responses. In the long run, it’s the only approach that will help your brand last in an AI-driven world. Don’t know how to optimize for AI? Definitely read this SEO vs AEO vs GEO guide to learn more.
How to Protect Your Brand from AI Poisoning Attacks
You can take some proactive steps to protect your SEO performance against AI poisoning. This means spotting problems early and having a clear plan in place to respond to attacks when they happen.
Detecting Data Poisoning in AI
Early detection is your strongest defense. You can stay ahead of potential issues by adopting a few consistent monitoring habits:
- Start with weekly AI audits. Test brand-related prompts across tools like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Perplexity. This helps you create a baseline and notice sudden changes in how your brand is described.
- Use brand monitoring tools as well. Platforms such as Mention, Brand24, and Google Alerts can help you see where your brand appears across the web, including forums and social media.
- Set up a prompt testing protocol. Create standardized comparison prompts, such as “Compare [your brand] to [competitor].” Record the responses each month to track any changes.
- Keep an eye on AI referral traffic. Separate your AI-related traffic in Google Analytics 4 so you can quickly catch unusual drops or unexpected patterns.
- Track cross-platform sentiment. Sentiment analysis tools can help you confirm that AI-generated content about your brand stays consistent and accurate over time.
Responding to AI Data Poisoning Attacks
If you do find signs of AI poisoning, it’s important to act quickly and stay organized. Here are a few ways you can respond effectively:
- Document everything. Take screenshots of suspicious responses, note timestamps, record the platforms, and save the exact prompts you used. Keep a running log of when the issue appeared and how it has changed.
- Report your findings to the AI platforms involved. Reach out to teams at OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google through their official support channels. Share clear evidence and request an investigation.
- Amplify accurate information. Publish authoritative, well-sourced content on your website, social media, and trusted third-party platforms. This helps ensure that AI systems pull reliable data during future training cycles.
- Engage legal counsel for serious cases. For defamation or financial harm, attorneys who specialize in digital rights and intellectual property can guide you.
- Work with your PR team. Prepare messaging that addresses customer concerns if misinformation starts circulating. Being open about the situation can actually strengthen trust when handled with clarity and confidence.
Final Words
AI poisoning is a serious concern for brand visibility and reputation, especially now that consumers increasingly trust AI platforms. Weaknesses in Large Language Models can be manipulated in ways similar to the traditional black hat SEO tactics. However, sustainable success comes only with ethical SEO practices.
Working with seasoned SEO professionals can help you stay visible in both traditional search and the new wave of AI platforms. At PNC Logos, we offer comprehensive SEO services to help you future-proof your digital presence against evolving threats. All while helping you stay ahead of the competition. Contact us now to get started!
Read more -
 December 05 2025
December 05 2025
Real Estate SEO Strategies to Rank Higher and Increase Your Property Sales
The new wave of home buyers is extremely tech-savvy. They rely heavily on online platforms when searching for the perfect place to live.
It’s true!
A recent REsimpli survey shows that 97% of buyers start their home search on the internet. And 88% still lean on real estate agents when it’s time to make the purchase.
For agents and real estate businesses, this is a huge opportunity. Strong online visibility can put you in front of a large volume of high-intent buyers who are ready to take action.
Real estate SEO services help your website rank higher in both organic and local search results, making it easier for serious buyers to find you.
In this guide, you will learn what SEO for real estate websites is. You’ll also get practical tips to help you dominate SERP rankings and attract more clients.
What is Real Estate SEO?
Real estate SEO is the process of optimizing a real estate website and its content so it ranks higher for location-based and property-focused searches. When you do it well, you can attract qualified leads who are already looking for homes or real estate services in their area. And you can do it without relying on paid channels like Google Ads.
At its core, this approach focuses on creating valuable content that targets the exact terms people type into Google. It also makes sure Google can easily crawl your site and display your pages in the SERP. However, the results don’t show up overnight. It can take months before you can see real traction. But with consistency, it can become one of the strongest channels for generating high-quality leads for your real estate business.
Why Does SEO Matter for Real Estate Businesses?
SEO of real estate plays a major role in helping homebuyers find your website before your competitors’. Here’s how SEO specifically helps real estate businesses.
1. Generates More Motivated Leads
SEO brings traffic from the people who are already searching for solutions to their real estate needs. They’re warmer, more intentional, and far more likely to convert than leads from outbound tactics. So, instead of chasing uninterested prospects through cold outreach, SEO can put ready-to-act buyers and sellers right in front of you with minimal effort.
2. Increases Traffic and Revenue
Effective SEO for real estate marketing can drive consistent organic traffic to your website by ranking for relevant keywords your target audience uses. This increased visibility directly means more leads and more closed deals. In fact, according to Search Engine Journal, 49% of marketers believe organic search delivers the highest ROI among digital marketing channels. Moreover, a study by Backlinko shows that the number 1 ranking page on Google gets nearly 27.6% of all clicks. This makes SEO non-negotiable for attracting more traffic.
3. Provides Long-Term Sustainable Growth
Paid advertising can help you generate leads with continuous funding. Meanwhile, SEO creates lasting results that compound over time. Once your pages secure strong rankings, they can continue attracting traffic with minimal upkeep. This gives you a steady and predictable flow of leads, something every real estate business needs to grow consistently month after month.
10 Steps to Implement SEO for Real Estate
Now that you know why SEO is crucial for a real estate website, here are the 10 must-know real estate SEO tips to improve your rankings and attract high-converting leads.
1. Do Keyword Research
Your SEO strategy begins with finding real estate SEO keywords. This is where you figure out the exact words and phrases your audience types into search engines when they’re looking for properties online. Some of these terms are short, usually two or three words. These types are more general and guide your content’s main topic. They also have a high search volume and high competition.
The best SEO keywords for a real estate agency with a newer website are usually long-tail keywords. These are more descriptive phrases that don’t get as much traffic, but they convert better. Because they’re so specific, they’re usually easier to rank for and attract more qualified leads. Here’s a graph that shows how these keywords compare to other search terms.

To find real estate keywords for SEO, you can start with simple tools like Google’s autocomplete feature. Another method is to study competitor websites and find out which keywords are driving their traffic.
When researching keywords, make sure to balance primary terms like “real estate agent in [a specific city]” with secondary phrases that address specific client needs. Prioritize local search terms with reasonable difficulty and decent search volume. This is because 46% of searches on Google have a local intent, as reported by Backlinko.
2. Understand Your Competition
Once you have your keywords, you need to analyze which websites are currently ranking for your target keywords and what makes them successful in these rankings. Your goal here would be to understand which strategies are working for your competitors, their digital marketing gaps, and the mistakes that could affect your rankings. To understand this, you need to identify what types of content your competitors are publishing, how they structure their pages and website, and which keywords are driving most of their traffic.
3. Create High Value Content
When it comes to real estate SEO marketing, content provides the main bulk to help your site show up in the search results. Anyone can create content. But yours should provide real value to your target audience so they can trust your site and actively seek your services. Their behavior will also signal to Google that you are credible enough to rank high in the search results.
Quality content satisfies two audiences simultaneously: search engines that need to understand your page’s topic, and humans searching for information to solve their real estate challenges. To write content that matches user intent, you need to understand what people actually want when searching specific phrases. For example, if someone searches “how much does a house cost in Florida,” your content can give them a clear idea with calculation steps and pricing factors.
Working with the best real estate SEO company can help you create high-value content that meets Google EEAT standards and ranks higher in SERPs. Some tips for creating valuable content include:
- Create one content page around one keyword.
- Place the primary keyword naturally in titles, headings, meta descriptions, and body.
- Use proper heading tags, break long paragraphs with images, and use bullet points.
- Highlight your expertise through credentials, achievements, and professional bio information.
- Offer unique perspectives from your real estate experience.
4. Optimize Property Listing Pages
The next step in real estate SEO strategy is to optimize your property listing pages. These are dedicated pages that showcase each property available for purchase or lease. Optimizing these pages helps you attract buyers who are in the final stages of the sales funnel. At the same time, you can provide comprehensive information needed to nudge them toward making a final decision.
Here’s what you need to do:
- Use the full address in the title tag, H1, and URL.
- Write a 300 to 500-word description highlighting lifestyle benefits.
- Add high-resolution photos, virtual tours, floor plans, etc.
- Include schema markup for RealEstateAgent and Property features.
- Place a prominent contact form button above the fold and integrate instant chat.
The best bet here is to work with a real estate SEO agency that offers on-page optimization. This will help you effectively showcase your content to potential buyers and sellers.
5. Perform a Full Technical Audit
In real estate website SEO, a technical audit gives you a clear look at how well your site is working behind the scenes. You want to be sure everything loads quickly. According to data from Portent, a page with a 1-second loading time converts 2.5 times better than one with a 5-second loading time.
You also want to make sure your site is free from issues that can block search engines from crawling your pages. This step is essential. If the technical foundation is shaky, even the best content or keyword strategy won’t deliver results because search engines won’t be able to access or interpret your site properly.
Use tools like Ahrefs Site Audit to identify technical issues affecting your site. As you do so, check for:
- broken links
- 404 errors
- duplicate content
- slow load speeds
- missing sitemaps and SSL security certification.
Once you identify the issues, prioritize fixing high-priority issues first, particularly those affecting crawlability and indexing. To do this:
- Address canonical tag problems
- Optimize images to reduce file sizes
- Ensure your robots.txt file is configured correctly.
6. Optimize for Mobile Searches
According to a report by the National Association of Realtors, 73% of all buyers use a mobile phone or tablet when searching for information about a home. Optimizing for mobile devices means that your website can be navigated seamlessly on these smaller screens. Moreover, Google uses a mobile-first approach for indexing, which means it crawls websites primarily using mobile bots.
You can make your website mobile-friendly by using a responsive design that automatically adjusts layouts, text, buttons, and images based on the type of device. In addition to this, here’s what you can do:
- Compress images before uploading
- Embed videos instead of hosting them directly on your server.
- Implement hamburger menus for clean navigation
- Ensure buttons aren’t positioned too close together to prevent accidental taps.
- Verify pop-ups don’t interfere with mobile browsing experiences.
7. Claim and Optimize Your Google Business Profile
Your SEO strategy isn’t complete without local SEO for real estate agents. This involves optimizing your website for location-based searches or those that include the name of a specific region or neighborhood. Creating and optimizing your Google Business Profile is the best way to rank for these searches.
For example, when you search for “real estate agents in Orlando,” the results will show the top three local businesses that have a strong Google Business Profile for real estate local SEO. These three listings, along with their Google Maps locations, are called the Local Maps pack. Securing one of these lucrative spots will dramatically increase your site’s visibility. And you won’t have to compete with established real estate directories that rank higher in regular organic results.

To optimize your Google Business Profile, make sure to complete every section thoroughly:
- Include your business name, address, phone number, website, hours, and category.
- Add high-quality photos regularly.
- Encourage satisfied clients to leave reviews.
- Utilize Google Posts to showcase listings and keep your profile active.
You can also take advantage of a real estate SEO consultant with expertise in local SEO. They can claim and optimize your GBP on your behalf, so you show up at the top of local searches and land more projects.
8. Use Schema Markup
The next step in real estate agent SEO is to use Schema markup. It is structured code added to your website’s HTML that helps search engines accurately understand and categorize your content. This makes it easier for clients to find relevant information much faster. It also gives search engines explicit details about your properties, agents, and business data, things that might get overlooked on their own. As a result, you can increase your chances of showing up in rich snippets, which can significantly boost your visibility and conversion rates.
You can implement three primary schema types for real estate websites:
- RealEstateListing for property pages with details like property type, floor plans, and price
- RealEstateAgent for agent profiles with names, service areas, and licenses
- LocalBusiness for company information like address, hours, and services offered.
9. Create High Quality Backlinks
Backlinks are a link-building strategy in which you gain links from other websites that point back to your real estate site. Whether you are an agency or working on SEO for real estate investors, backlinks are like “votes” that tell search engines that you’re doing something right. When you’re building links, focus on high-quality backlinks from well-reputed websites. These links carry a significant ranking weight of up to half of the overall impact. So they’re critical if you want to compete for keywords with high competition.
These links also send referral traffic from linking sites straight to your business. Apart from this, make sure that your backlinks come from sites relevant to your real estate business, rather than purchasing them from unverified and irrelevant sources.
10. Regularly Track Your SEO Performance
Launching your SEO strategy is only step one. You’ll need to monitor how your efforts perform over time so you can make decisions based on real data, not just guesswork. Google Search Console is a great tool for checking how your site appears in search. Keep an eye on metrics like average CTR and keyword rankings. You can also use Google Analytics for more in-depth information, such as user behavior, time spent on pages, and their navigation patterns. Over time, these insights will help you strengthen your rankings and improve the ROI of your SEO strategy.
Final Words
In the long run, real estate SEO can bring in high-value leads consistently without depending only on paid ads. When you apply the right strategies, you’ll see stronger organic rankings and build more local authority through your Google Business Profile and quality backlinks.
Just remember that SEO takes time. However, working with a professional can help you make this process more effective and get better results. At PNC Logos, our team of real estate SEO experts understands how competitive the industry is. We use effective SEO strategies to get your business to the top of search results. If you want to get ahead of your competition, contact us today
Read more -
 November 28 2025
November 28 2025
Facebook Logo: History, Evolution, and Current Brand Guidelines
When you think of Facebook, that small “f” against the blue background instantly comes to mind. But why does this brandmark feel so familiar?
It’s not just because you’ve seen it a million times. But it’s the subtle and careful updates over the years that, while aligning the design to evolving trends, preserved the original design elements of this iconic brandmark. These intentional changes helped the monogram stay recognizable to users of every generation.
But, where did the Facebook logo begin? And how did it get to where it is today?
This article shares everything you need to know. You’ll learn about the evolution of the Facebook logo, its key design elements, and more.
Facebook Logo History: From the First Facebook Logo to the Current Design
The Facebook logo design started in a Harvard dorm when four computer science students created the website. Among them, the name that stands out the most, and the one we all still associate with Facebook, is Mark Zuckerberg. Since then, both the website and its brandmark have gone through a lot of changes. Interestingly, it wasn’t even called Facebook then, and definitely did not have its signature blue logo.
Here’s a deep dive into the Facebook logo evolution over the years.
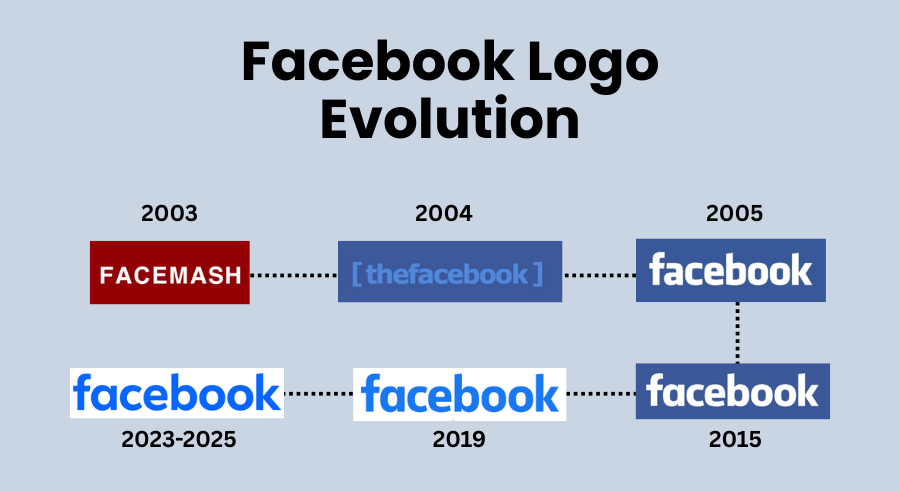
The Original Facebook Logo 2003

In 2003, Mark Zuckerberg was a second-year student at Harvard, who, after a night out, set out to create a website called Facemash. It was designed around the idea of comparing and voting on which picture was “Hot” and which was “Not.”
Thanks to Zuckerberg’s idea of hacking into Harvard’s security network to get students’ ID images, the site was shut down a few days later. But before it did, Zuckerberg had given his new site a logo – white uppercase letters “FACEMASH” sitting against a deep red rectangle background. This very logo, although short-lived, set the foundation for the later versions of the Facebook wordmark.
The Facebook Logo 2004

The demise of his newly invented website did not discourage Zuckerberg, and neither did almost getting expelled from Harvard. On February 4, 2004, he launched a new website called “TheFacebook.” The name came from the physical directories (also called Facebook) that were given to Harvard students to help them get to know each other better.
That’s when the first Facebook logo was born. It was still a minimal wordmark logo, but now ‘blue’ came into the scene. The logo consisted of lowercase letters “thefacebook” in light blue, enclosed by square brackets, and set against a darker blue rectangle.
Growing Recognition: Facebook Logo 2005 – 2015

2005 came with great tidings for the then-just-growing social network. The platform had expanded beyond a few colleges and was gaining serious popularity. At this stage, the company needed a brand name that could grow with it, something that didn’t tie it only to college directories.
That’s when “thefacebook” dropped the “the” and became simply “Facebook.” The name change was a big deal. The company even spent over $200,000 just to secure the matching domain, facebook.com.
With the new name in place, the company now needed to replace Facebook’s old logo. The design shifted to a lowercase wordmark using the Klavika font. The letters were softened with rounded corners and scaled to occupy more space inside the blue rectangle. Additionally, its angled ascenders added a sense of motion, which helped an otherwise simple mark feel more alive.
Minimalist Facebook Logo 2015 – 2019

It wasn’t until 2015 that the company decided to give its wordmark logo another refresh. Subtle changes were made to the original typography to align it with modern logo design trends and better suit a mobile-first world. The typeface for the Facebook new logo was now slimmer and rounder, with the ascender from “a” removed.
According to Eric Olson, the creator of the company’s original Kavika logo, “The original is dark, condensed, and compact.” He further added, “The thing that I really wanted to bring over to the new one was a single story ‘a.’ I felt like there was a point of entry there to streamline a bit.” With changes to one letter, the logo now felt more approachable and friendlier.
The New Era: Facebook Logo 2019 – 2023

In 2019, Facebook made significant changes to its logo’s color palette. The blue wordmark was now placed against a neutral background. In other words, it had now switched from a negative to a positive space logo. Moreover, the deeper blue shade was replaced with a brighter blue, and inter-letter spacing was improved.

In addition, Facebook also introduced its new company brand in 2019. The goal was to distinguish the social app from the corporate umbrella. The logo, while still named Facebook, included block letters slimmer and more spacious than the app’s logo. The primary color for these was the same bright blue as the app. But the logo could change colors depending on where it appeared, such as on Instagram, WhatsApp, and Oculus.
The Facebook Logo 2023 – Present

Another subtle change to the logo’s typeface came in 2023. The font was still a custom version of the sans-serif typeface, but more rounded and slimmer than the previous versions. The color was still blue, but a very subtle, deeper shade. And the same wordmark still represents the platform today in 2025.
Evolution of the Facebook “f” Logo Icon

Much like its wordmark, subtle upgrades were made to the monogram Facebook logo through the years. But most of these shifts were small and intentional.
The first version appeared in 2005. It had a square icon with rounded, layered borders and a small “f” pushed slightly to the right. The reflective highlight in the background perfectly suited the early Web 2.0 aesthetic.
By 2009, the Facebook logo icon shifted to a deeper, more uniform blue and adopted a more defined square shape. The highlight dropped toward the bottom, and the “f” looked a bit more vertically balanced.
For over ten years, the changes remained subtle. Then, the most significant upgrade came in 2019. The square became a circle to match modern logo standards, and the background shifted to a bright two-tone gradient.
This circular “f” icon held strong for nearly a decade. Then, in 2023, Facebook refreshed it once more with a new color palette – still blue, just a bit more blue.
But Meta had a good explanation for this subtle change:
“Our intention was to create a refreshed design of the Facebook logo that was bolder, electric, and everlasting… We’ve done this by incorporating a more confident expression of Facebook’s core blue color that is built to be more visually accessible in our app and provides stronger contrast for the “f” to stand apart.”
The same monogram represents the Facebook logo in 2024 and the current Facebook logo in 2025.
Transition to Meta Branding

The 2019 block-letter Facebook logo was replaced by Meta in October 2021. It was when Facebook reorganized its parent company to reflect its bigger vision that went far beyond social networking. This move set the stage for the company’s push into the “metaverse,” which stands for a more immersive and interconnected digital world.
The Facebook Meta logo aligns perfectly with this idea. The infinite loop–style mark that reads as both an “M” and a symbol of endless possibilities. The continuous form represents themes of connection and the future of digital interaction. The wordmark that accompanies it is also clean and modern to keep the look cohesive.
Inside the Facebook Logo: Key Design Elements
The main design elements of the Facebook logo include a custom typeface, “Facebook Sans” for its wordmark, the “f” monogram icon, and medium blue as its primary color. Let’s look at the Facebook logo specs and design in more detail.
Facebook Logo Font
The official Facebook font design is the custom version of sans-serif Klavika, created by Eric Olson. The typography of the Facebook logo over the years has changed significantly. The dynamic letters have been replaced with a more rounded and minimal design.
Facebook Logo Color
Facebook logo color code is #4267B2, which is a cooler blue shade with RGB values of 66, 103, and 178. According to a New Yorker post in 2010, Mark Zuckerberg has red-green color blindness but can easily distinguish shades of blue. This is popularly associated with the choice of Facebook’s logo color palette.
Facebook Logo Meaning
The consistent use of the lowercase letters in the Facebook logo perfectly represents the platform’s welcoming and friendly environment. The signature blue color stands for trust and reliability. These qualities make it a great choice for a platform built on communication and personal connection.
That’s one of the major reasons why Fortune 500 companies prefer using blue in their logos, according to Canva.
Company Behind the Logo: The Impact of Facebook Today
Facebook’s influence today is massive, and a lot of that comes down to its iconic logo. Statista reports that Facebook reached two billion active users in just over 13 years. This makes it the third fastest social platform to reach that milestone.
A more recent study shows that in the fourth quarter of 2023, Facebook remained the most used online social network worldwide with over 3 billion monthly active users. Considering the global population is over 8 billion, that’s a massive number of people staying connected through the platform.
Final Words
Although the Facebook logo has undergone upgrades over the years, the brandmark has remained welcoming and familiar. It’s the embodiment of small yet strategic changes that can keep a brand relevant without affecting its identity. You can take it as an example to design your own brand logo.
At PNC Logos, we help you make this easier! We know a logo is more than just a design. It carries your brand’s very essence in its visual identity. If you want a logo that truly reflects your identity and connects instantly with your audience, contact us now!
Read more -
 November 25 2025
November 25 2025
The Ultimate Mascot Logo Guide for Brands: What to Know Before You Start
People don’t remember brands. They remember faces. Even when that “face” has fur, antennae, or a goofy, oversized smile.
That’s the entire cheat code behind a great mascot logo. It goes past logic and connects directly to emotion.
If you’re ready to create your own mascot logo, this guide explains the mascot logo meaning with examples and walks you through the process in practical steps.
What is a Mascot Logo?
A mascot logo is a brandmark that includes an illustrated character. This could be a person, an animal, a cartoon figure, or any creative character that reflects the brand’s personality. The mascot logo definition usually includes pairing this character with the brand’s wordmark logo so people can easily connect the visual with the business name. Because the character essentially becomes the “face” of the brand, it helps audiences quickly recognize and remember the business whenever they see its products, social posts, or messages.
Why Choose a Mascot Logo Design for Your Brand
Mascot logos help your audience feel more connected to your brand over the long term. And there’s plenty of research to support the importance of the mascot logo for businesses.
1. Higher Profit and Emotional Impact
A study from the Moving Picture Company found that mascots can boost profit and emotional engagement by up to 41%. They also make brands 37% more competitive. In other words, mascots help your brand stand out and engage customers on a deeper level.
2. Better Attention and Recall
A study published in Research Space shows that 59.5% of people pay more attention to brands with mascots. Another 56.7% find it easier to recall brands that have mascots or characters. Needless to say, mascots make your brand more noticeable and memorable.
3. Greater Market Share Growth
Research by global marketing research firm System1 reveals that campaigns using mascots can increase market share by 37%. This makes it clear that mascots strengthen marketing performance and help brands grow faster.
Mascot Logo Types (with Famous Brand Examples)
Your brand identity and target audience play an important role in determining the best mascot design. There are several common types of logos to consider. To help you visualize, here are some relevant mascot logo examples with the names of their brands.
1. Animal Mascot Logos
Animal mascot logos are based on real or stylized animal characters. And since most people associate animals with specific qualities, these types of brand marks can communicate the brand’s personality more effectively.
Think about Duolingo’s owl mascot logo, for example. Duo pops up in friendly, expressive poses that push users to stay motivated as they learn new languages.

Or look at the World Wildlife Fund’s panda, a calm and instantly recognizable symbol that naturally reinforces the organization’s mission to protect endangered species.

On the contrary, Lonsdale uses a walking, roaring lion mascot logo. Now, that’s the perfect way to project strength and courage for its boxing and martial arts audience.

Tiger mascots are also used in the fashion world. Kenzo’s tiger mascot logo includes the tiger head, paired with “Kenzo Paris.” It embodies a fierce energy suitable for the bold and exotic feel the brand is known for.

2. Cartoon Mascot Logos
Cartoon mascots are expressive and, therefore, instantly feel approachable. Even when the character style is playful, it can still be a smart move to use it to make your brand experience feel more human.
KFC does this well with its stylized portrait of Colonel Sanders, complete with his bow tie and warm smile. It showcases the brand’s familiar and welcoming personality.

Similarly, in Pringles, Julius Pringle portrays a lighter and fun-first personality. It has a round face, mustache, and upbeat expression to match the brand’s cheerful snack identity.

Another example is Mailchimp’s smiling Freddie the Chimp. It’s a minimal hand-drawn mascot that makes the platform feel accessible and less corporate while still aligning with its mission to simplify email marketing.

Reddit keeps things quirky with Snoo, the alien. This character is identified by an antenna and bright eyes. These features align with the site’s tech-driven and community-powered personality.

3. Vintage Mascot Logos
Vintage logo designs are inspired by illustration styles from the early 20th century. So they naturally give off a nostalgic feel. But more importantly, brands using this style of mascots feel more established and more trustworthy. Industries like automotive, snacks, and beverages usually use these retro mascot logos.
A classic example is Michelin’s Bibendum. Made of stacked tires, this oversized figure represents the brand’s mission to provide sustainable mobility solutions.

Planters is another great example. The company’s mascot, Mr. Peanut, is a dapper humanlike peanut. It personifies the brand’s mission of being premium and always “A Nut Above.”

4. Educational Mascot Logos
Educational mascots include the school or college mascot logos. These focus on school identity and spirit, which could be fun and friendly for younger students or fierce and commanding at the college level. Famous mascot logos in education are usually symbolic animals or illustrations that rally students and sports team fans.
For example, Boston College has a dynamic eagle mascot logo. It is the perfect symbol of their pride on campus and in games. The same can be seen in the bear mascot logos of Baylor University. The American Black Bear perfectly showcases the strength and spirit of the university.

5. Sports Mascot Logos
Sports mascots are quite similar to university mascot logos, but they are specifically used to represent a team’s strength and competitive energy. These can be powerful animals, mythical creatures, or action-oriented human figures driving the visual story.
You can see these in gaming team mascot logos. For example, the Carolina Panthers use a panther mascot logo. It shows a snarling panther head that captures the team’s fierce presence in the NFL. Similarly, the Minnesota Timberwolves use a wolf mascot logo. The howling wolf is set against a subtle forest backdrop – a perfect representation of the untamed spirit of the northern wilderness.

By examining these mascot logo design examples, you can identify the key elements of a successful brand logo. These can help you create the ideal character for your own business.
Key Design Elements of Successful Mascot Logos
Successful brand mascot logos aren’t created randomly. They materialize the very essence of the brand. At the same time, they resonate with the target audience and stick in people’s minds.
But what exactly makes a mascot logo style unique? Here are the golden rules of logo design to be aware of.
- Instantly Recognizable: A well-designed mascot will stand out the moment you see it. Simple shapes and clean lines help it maintain its appeal at any size and in any format. Even without color, it should be readable.
- A Personality That Matches the Brand: A mascot’s tone and attitude need to feel intentional and consistent. Whether it’s playful, calm, bold, or refined, the character should communicate what the brand stands for.
- Flexible and Easy to Adapt: A mascot should work seamlessly across all formats, sizes, and applications. It must stay recognizable when fully illustrated or shrunk down into an icon.
- Builds Human Connection: Expressive features and storytelling cues help make a mascot logo feel more alive. It should be able to increase trust in your brand and encourage more engagement.
- Designed to Last, Not Follow Trends: Trendy styles age quickly. Your mascot should be timeless and remain a meaningful symbol as the brand evolves. You can still make small updates to make sure your logo doesn’t feel outdated.
Definitely check out modern logo design examples to know how logo designs have evolved over the years.
How to Make a Mascot Logo Your Audience Will Remember
Creating the best mascot logos is a strategic process. You need to understand what your brand stands for and how to use visual storytelling to embody its very essence in your character.
A successful mascot logo design process includes the following steps.
Step 1. Know Who You’re Competing
Before you start the design process, take a look at your competition. This will help you design a character that is unique to your brand and does not blend in. Moreover, once you notice the mascot logo trends in your industry, you can align your character to your industry’s design expectations.
When researching your competition:
- Analyze the character types, design elements, and color palettes.
- Identify the recurring elements and avoid those as they can feel predictable.
- Brainstorm what your mascot can do differently to avoid being generic.
- Outline ideas that make your brand genuinely different.
Step 2. Understand Your Brand’s Core Values
At this stage, you will know exactly how to distinguish your mascot from your competition. Now, you need to align your mascot’s personality to your brand’s mission and purpose. This will affect how people perceive your brand and guide the tone you want to communicate. When you’re clear about these principles, you can make your mascot logo design feel more intentional.
Ask yourself these questions to establish your core values:
- What are the top three qualities people should associate with your brand?
- What does your brand offer emotionally, not just functionally?
- How are people already describing your business?
- Which personality do you want your brand to project?
Once you have your answers, you can envision how your mascot’s personality should look and feel.
Step 3. Give Your Mascot a Strong Personality
Mascots go beyond just drawing a fun character. You want it to have a personality that conveys your brand’s message without saying a word. For example, you might use the personification of a fox to represent your brand as clever or wise. But the way you portray it changes everything.
Instead of a plain fox character, it could look cheerful, brooding, sarcastic, or mischievous – whatever best describes your brand. Think about how you want people to feel when they see it. And let those traits guide the character’s overall behavior and tone.
Step 4. Choose a Character That Fits Your Brand
After deciding how your brand should feel, you need to establish what it should look like. You can draw mascot logo inspiration from any character, like an animal, a cartoon, or a fantasy figure. But whatever you choose, make it fit your brand identity.
While you will only use a specific part of the mascot in the logo, like a face drawing or the character’s silhouette, later on, it can take the form of a 3D character to use in your marketing materials. So, design the character’s entire personality, from its actions to its tone, to keep everything consistent and streamlined.
Step 5. Sketch Out Your Ideas
At this point, you will have a solid foundation to kickstart the design process. Start by sketching your mascot logo ideas. And while you do that, be as creative as possible. Don’t focus on getting it right or knowing exactly what you want to create.
Sketching would be your creative playground to explore and brainstorm ideas freely. Draw out different poses, costumes, and expressions. These will help you get a complete picture of how your character should behave. You can also look at the logo sketches of famous brands for inspiration.
Step 6. Choose a Color Palette
After you’ve done your drawings, choose a color palette that fits your mascot’s personality. Colors are a powerful tool to communicate a certain image of your brand. Popular mascot logos always choose their palettes intentionally. Just remember that whatever colors you use, make sure they align with your brand’s primary color palette.
Step 7. Make Your Design Unique
Drawing the character is only one part of the equation; the design itself should be singular enough to be memorable. So, think outside the box. Go for exaggerated shapes or oversized elements like large glasses or shoes, and out-of-proportion limbs or belly.
But since you would need to combine the mascot with your brand’s wordmark, avoid complex shapes. Keep your design simple and legible. The overall design of the character should make people feel something. At the same time, it should align with your brand identity.
Final Words
A well-designed mascot logo brings your brand’s story and values to life. But it takes strategy, clear branding insight, and a series of intentional design choices. The process can get detailed and a little overwhelming, which is why an expert mascot logo maker can make a huge difference.
At PNC Logos, we help brands like yours design memorable mascot logos that resonate with your audience and carry your brand’s story. Contact us today to bring your mascot ideas to life!
Read more -
 November 14 2025
November 14 2025
Hyperlocal Reviews: What They Are and How to Use Them to Grow Your Local Business
Want your business to be the go-to spot in your neighborhood, not just another name on Google Maps? You need to think beyond a good star rating on Google or Yelp. Today, success depends on how strategically you use customer feedback to influence people closest to your location.
Hyperlocal reviews can help you do just that. These are not just testimonials. They are the key to building trust and placing your brand as an authority in your industry. This guide shows what these reviews are, why they matter, and how to use them to dominate your local market.
What are Hyperlocal Reviews?
Hyperlocal reviews are customer ratings and testimonials that show up when people search for businesses in a very specific area. For example, someone searches for “Best pizza near me?” or “AC repair in [my neighborhood].” With strong local SEO, the top 3 nearby businesses offering these services in a specific region can appear in Google’s Local Pack. Reviews from customers in the immediate area—called hyperlocal reviews—help strengthen a business’s relevance and improve its chances of appearing in these top results.
Unlike broader online ratings, “near me” reviews for businesses build a direct connection between people and businesses in a specific targeted area. They influence buying decisions and how communities find and choose their local favorites.

Why Reviews Matter for Local Businesses
Reviews are not just nice words from happy customers; they can shape how people see your brand and whether to trust you enough to buy. Here’s why they are critical for your business’s growth.
1. Reviews drive real-world visits
Mobile local search “near me” has significantly increased over the years. According to Google, 88% of people who search for a local business on their mobile phone end up visiting a related store within a week. Even more impressive, 60% reach out directly from the search results. When your business has strong local reviews, people see it as more credible and worth checking out.
2. Reviews shape your brand perception
Yelp reports that 70% of consumers rarely try a new business without reading reviews first. And DataReportal says 37.2% of online users aged 16-64 rely on reviews as their primary source when researching brands. So for local businesses, reviews are an essential part of your brand identity. They tell your story before you ever speak to a customer.
3. Reviews influence purchase decisions
Trustpilot found that 66% of consumers are often or very often influenced by reviews when deciding where to buy. BrightLocal adds that 42% of people trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations from friends and family. In other words, reviews have become the new word-of-mouth. They can make or break your business’s credibility long before a customer walks through your door.
How to Get Reviews for a Local Business
Now that we understand how powerful reviews can be, the next step is to actively earn them. Here are practical and ethical ways to encourage more customers to leave genuine reviews for your local business.
Optimize your Google Business Profile
To be eligible for your reviews to appear in Google searches, you need to claim and verify your Google Business Profile. It is a free listing that keeps your business visible in local searches. Once you’ve created your profile, you need to optimize it with comprehensive details of your business. This will ensure that customers can trust your brand and feel encouraged to leave Google reviews on your business profile.
Here are some details to include in your profile:
- Include your exact business name, address, and phone number.
- Write a clear and keyword-rich business description.
- Choose the main and secondary categories that best describe your business.
- Include a Q/A section to answer customer questions directly.
- Keep your hours and contact information up to date.
- Regularly post updates, offers, or events.
Get Listed on Other Relevant Sites
Besides Google Business Profile, you can list your business on other trusted platforms relevant to your industry. This can give your brand more visibility and increase the chances of generating customer reviews locally. In fact, data from BrightLocal shows that 74% of consumers use two or more review platforms when researching a business. However, make sure that your NAP details are consistent across all sites. This signals to Google that your business is credible, while also building trust with potential customers.
Here are some popular review platforms by industry:
- Restaurants: Yelp, Zomato, TripAdvisor
- Healthcare: Healthgrades, Practo, RateMDs
- Hospitality:com, Expedia, Airbnb
- Home Services: Angi (formerly Angie’s List), Thumbtack, Houzz
- Retail and Local Stores: Facebook, Trustpilot, Nextdoor
- Education or Training:com, Course Report, ClassCentral
Directly Ask Customers for Feedback
The simplest way to get more online business reviews is to just ask. Most satisfied customers are happy to share their experience. They just need a little nudge at the right time. The best moment to ask for a review is right after a positive interaction. This can be after completing a purchase, resolving an issue, or delivering a great service.
When requesting reviews:
- Focus on asking loyal or visibly satisfied customers first
- Never offer rewards or incentives, as it may violate platform policies.
- Follow up once, but avoid being pushy or repetitive.
Some ways you can request reviews directly include:
- Run a review email campaign after purchases or appointments.
- Ask for reviews on social media by encouraging followers to share their experiences.
- Use in-store reminders, such as QR codes on receipts or posters.
- Send thank-you messages with a gentle reminder to share feedback online.
Make it Easy to Leave Reviews
Most people won’t take extra steps to search for your business to leave feedback. So, keep the process effortless by providing a direct link to your review page in emails, messages, or social media posts. Make sure the entire process is simple, with minimal steps and clear instructions. This way, your customers will feel more encouraged to leave reviews and be more detailed in their feedback.

Keep Your Request Personal
Today’s average customer is constantly bombarded with emails and newsletters on a daily basis. Your review request needs to stand out to encourage action. The best way to achieve this is to personalize your emails.
You can do this by addressing the customer by their name. You can also reference their recent interaction with your brand to show how much value their individual experience.
For example, you could say, “Hello Maria, we hope you’re enjoying your recent home cleaning service. If you have a moment, please leave us a review to let us know how we did.”
Manage Existing Reviews Effectively
While attracting new reviews is crucial, how you manage existing ones is equally important. Thoughtful responses show that you value feedback from your customers. These also build trust with new customers and encourage more people to share their responses. When responding to reviews, make sure to address both positive and negative feedback.
Review management for small businesses typically includes:
Responding to Positive Reviews:
- Thank the customer personally.
- Mention specific details from their experience.
- Reinforce your commitment to quality.
- Invite them to return or engage further
- Keep the tone genuine and professional.
Responding to Negative Reviews:
- Respond promptly (within 3-4 days at max)
- Acknowledge the customer’s concern
- Apologize sincerely when appropriate
- Offer a practical way to resolve the issue
- Avoid defensive language.
- Show empathy and a willingness to improve.

With these key strategies, you can motivate customers to share their experience with your brand. This will improve local business ratings of your brand and help you dominate the local market.
Key Benefits of Local Reviews to Inspire Your Marketing Strategy
Local reviews provide more than just feedback. They are the ultimate resource to increase your online visibility and grow your business. Here are the key benefits they offer.
1. Boost Your Local Search Rankings
Local SEO reviews are one of the factors that can help you appear in the Google Maps pack (the top 3 local businesses). Collecting reviews on multiple platforms with a positive sentiment signal to Google that your brand is authentic and helpful. Reviews also naturally include long-tail keywords that you may not find in your keyword research. As a result, reviews influence local SEO and help your business appear in more nuanced local searches.
2. Increase Visibility in AI-Driven Responses
Research by BrightLocal found that AI tools and large language models use reviews from platforms like Google and Yelp to recommend businesses. If you have lots of recent and positive reviews, you can increase your chances of showing up in AI responses and get more visibility for your business.
3. Build Trust in Your Brand
Hyperlocal reviews include honest feedback from your community. These reviews show what customers value about your brand, converting them into your brand advocates. As Jeanne Bliss, the co-founder of The Customer Experience Professionals Association, says:
“Customers who love you will market for you more powerfully than you can possibly market yourself.”
Common Mistakes to Avoid With Local Reviews
Even with a solid strategy, a few missteps can hold you back from positive results. Here are some common mistakes to avoid in your local reviews strategy.
- Waiting Too Long to Ask for Reviews
If you wait days or weeks after a purchase or service, customers are less likely to leave feedback. Therefore, make sure to ask for reviews right after a positive interaction, while the experience is still fresh in their minds.
- Being Too Pushy
Bombarding customers with review requests can feel annoying and may backfire. Keep your requests polite and optional. Give people space to respond when it works for them.
- Forgetting to Follow Up
A lot of customers plan to leave a review, but simply forget. A gentle, well-timed reminder can bump up your response rates without coming across as spammy.
- Not Taking the Conversation Offline
Some problems are too detailed for public reviews. Invite unhappy customers to discuss issues offline – over the phone, email, or in person. This helps solve the problem without creating a public dispute and protects your online reputation.
How to Utilize Hyperlocal Reviews For Business Growth
When used strategically, local reviews can help improve your digital marketing campaign and build community trust in your business. Here’s how to make them work for you:
Identify and Analyze Trends
Monitor your reviews regularly to spot patterns in customer feedback. You can use a local business reputation management tool to identify and track feedback. Look for recurring themes, what customers love, and what frustrates them. These insights can highlight areas where you might need to improve your team’s performance or internal processes.
Informed Business Decisions
Think of reviews as a form of ongoing market research. They can give you real-time data to make customer-driven decisions that fit your audience’s needs. For example, if you consistently see requests asking for a specific product or feature, that’s a clear sign to consider adding it to your lineup. Such data-driven decisions can make your brand more helpful to customers.
Turn Reviews Into Marketing Assets
You can highlight positive local search marketing reviews across all your marketing channels. This can include your website, Google Business Profile, and social channels. Real customer voices build trust faster than ads. You can pair them with video testimonials to create authentic content that drives conversions.
Final Words
Hyperlocal reviews can make a big difference for your local business. They build credibility with potential customers and give you useful insights into what your audience really thinks.
Start by making sure your business is listed on Google Business Profile and other local directories that matter in your area. Actively ask for reviews and respond promptly to all feedback.
If you want to make the most of your efforts, consider working with a local marketing expert. They can fine-tune your review strategy and help you get more traction from the feedback you’re already getting.
Read more -
 November 07 2025
November 07 2025
SEO for Plumbers: The Ultimate Guide to Growing Your Plumbing Business Online
Your plumbing business has skilled technicians. But no steady flow of customers to grow your business. Meanwhile, competitors with polished websites are getting the calls that once came your way.
The solution? SEO for plumbers. When done right, SEO can help your business appear when homeowners search online for plumbing services. This guide shares the most effective SEO strategies to help you boost your rankings and attract more customers online.
What is SEO for Plumbers?
SEO for plumbing companies refers to the process of improving a plumbing company’s website so it appears higher in search engine results when people search for plumbing-related services online. This means that if a homeowner searches for “emergency plumber near me,” an SEO-friendly website will appear in the top 10 results on Google’s first page.
But how to rank your plumbing business on Google? This involves several interlinked SEO strategies:
- Local SEO: Optimizing for searches in your business’s local area.
- Keyword Research: Finding search words or phrases your customers use.
- Content Marketing: Creating helpful articles, guides, and service pages.
- On-page SEO: Improving page elements and website content.
- Technical SEO: Enhancing site performance, structure, and mobile usability.
- Link Building: Backlinks from trusted and relevant websites.
Why Does SEO Matter for Plumbing Companies?
SEO helps plumbing companies boost their online visibility, attract local customers, and win more service calls. Here are more specific benefits it offers:
Ace the Competition
According to IBISWorld, there are over 130,000 plumbing businesses in the U.S. This fierce competition makes it difficult to stand out. Plumbing marketing strategies like SEO help your company appear first when potential customers search online.
Improve Online Visibility
Data from SOCi shows that 83% of Americans use search engines to find local businesses each month. SEO makes sure your business shows up in their search results and generates more leads.
Capture More Traffic
According to Backlinko, the #1 ranking page on Google gets 27.6% of all clicks, while only 0.63% of people click results on page two. In another study, Backlinko reports that 50% of Google searchers take only 9 seconds to click on a result. Best SEO for plumbers helps you secure top spots and capture the most traffic.
Land More Plumbing Jobs
Data from WebFX reports that 80% of local searches result in conversions. Moreover, Google data shows that 76% of consumers who search for “near me” visit a business within a day. Plumbing company local SEO ensures your business ranks high in local queries, turning those searches into more projects.
Local SEO for Plumbers to Attract More Local Customers

Local SEO means improving your online presence so your business appears in top search results when someone nearby searches for what you offer. For example, when someone searches, “water heater near me,” Google shows the top 3 well-optimized local profiles on Maps. This is called the Local Map Pack. A new study by Backlinko shows that 42% of local searchers click on results inside the Google Maps Pack.
Here are some local seo tips for plumbers to appear in this lucrative spot.
1. Optimize Your Google Business Profile
When determining the map pack rankings, Google considers three things: how relevant your business is to a search query, distance from the location of the search query, and your business’s reputation. Google Business Profile acts as the main source for this data. It is your company’s free Google listing and an essential part of affordable SEO for plumbers.
You can claim and complete your business profile yourself. Or, ask a plumbing SEO company to optimize it on your behalf. Typically, you need to add the following information:
- Clearly describe your business, target audience, location, and local keywords.
- Keep your business name, address, and phone number identical everywhere.
- Link each business location to its specific webpage, not the homepage.
- Select an accurate main category and add relevant secondary ones.
- List your products and services clearly in the provided sections.
- Upload high-quality photos showing your team and space.
- Regularly update hours and details to maintain accurate information.
2. Build a Local Citation Network
Local citations are integral in SEO for plumbing business growth. These are mentions of your business on trusted platforms and local directories. Most websites use your business’s name, address, and phone number (NAP) in their mentions.
Why do citations matter? Multiple consistent NAP mentions of your business tell search engines that your business is legitimate and reliable. In fact, a BrightLocal study shows that 62% of people don’t use a business if they find incorrect information online.
3. Collect Reviews and Testimonials
Customer reviews are powerful ranking and trust signals for local businesses. In fact, a survey from local SEO experts reports that High Numerical Google ratings of 4-5 are the 6th most important local pack ranking factor. So, make sure to encourage customers to leave reviews on Google, Yelp, and other directories. Respond timely to all reviews – both positive and negative.
9 Plumbing SEO Tips to Stay Visible in Organic Search Results
While plumbing local SEO can help you rank for the Google Maps Pack, you can also utilize SEO to show up in organic results. These are the non-paid webpages ranking below the local pack.

Here are 9 SEO strategies that can help you show up in organic results.
1. Find Plumbing-Related Keywords
Keywords are the words and phrases people type into Google when they’re looking for plumbing services. The right keywords will help your website show up in those searches. You’ll want to add these keywords naturally throughout your site. This would include titles, headings, meta descriptions, and image alt text.
But, how do you find the best keywords?
Start simple. Use Google Autocomplete, Related Searches, or the People Also Ask section. You can also use dedicated tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or Ubersuggest. Otherwise, companies providing SEO services for plumbers can help with keyword research.
When you’re choosing keywords, keep four things in mind:
- Search volume: how many people are searching for it
- Competition: how difficult it is to rank
- Relevance: how closely it matches your services
- Search intent: what users actually want to find
The following are types of keywords to focus on:
Local Keywords
These combine a plumbing service with a specific location. For example, “emergency plumber in Orlando” or “drain cleaning near me.” Use them in your page titles, meta tags, location pages, and your Google Business Profile to increase local visibility.
Service and Industry Keywords
These describe your core offerings, like “water heater installation” or “pipe repair services.” They tell search engines exactly what your business does. SEO for plumbing contractors means using these keywords strategically on your homepage, service pages, and FAQs.
Long-tail Keywords
These are longer, more specific search phrases. Some examples include “how to fix a leaking kitchen faucet” or “best plumber for bathroom remodeling.” They usually have less competition and attract users with a clear intent to solve a problem. You can naturally weave these into blog posts, how-to guides, and FAQ sections to capture those niche searches.

Match Keywords to Search Intent
Search intent reflects what users truly want when searching online. When your pages align with the right intent, Google will position them higher in search results. Primarily, intent is of 4 types:
- Informational: People want answers (how to unclog a drain)
- Navigational: People are looking for a brand (ABC Plumbing website)
- Commercial: People are comparing options (best plumbing companies in Houston)
- Transactional: People are ready to hire (book a plumber near me)
2. Create Valuable Content
After identifying the right keywords and intent, you need to create content that targets them effectively. You can work with plumbing SEO experts to further ensure your content ranks higher and reaches the right audience.
You’ll need to create content for the following types of pages.
Homepage Content
Your homepage is the first impression people get of your business. So make it count. Clearly explain who you are, what plumbing services you provide, and which areas you serve. Use strong headlines and calls to action. Include trust elements like customer reviews, certifications, or testimonials. The goal is to help people instantly understand your value and encourage them to reach out.
Create Service and Location Pages
Create dedicated webpages for each service, such as drain cleaning, leak detection, or pipe repair. And if your plumbing business operates in multiple regions, create individual pages for each area. Add local keywords, maps, and examples of past work done in that specific location. These pages will strengthen your local SEO. As a result, your business will appear in searches from customers who are ready to hire.
Build a Plumbing Blog
Blogging is a key strategy in SEO for plumbing companies for plumbers. It is your chance to target customers with informational intent, such as those searching for solutions to their problems. Therefore, answer common questions like “Why is my water pressure low?” or “How can I prevent frozen pipes in winter?” to build trust. Regular blogs will also keep your site active and improve your rankings.
3. Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Title tags and meta descriptions are small chunks of text that define the page’s title and summarize its content in search results. These are key elements of on-page plumbing company SEO. Tips for writing these include:
- Meta titles should be under 40 to 60 characters
- Keep meta descriptions under 160 characters.
- Include primary keywords.
- Focus on encouraging users to click.
4. SEO-friendly URLs
Your page’s URL should be simple, clear, and descriptive. Use lowercase letters and add hyphens between words (not underscores). You should also include your target keyword. But make sure it’s short and relevant to the page. For example, a page about drain cleaning services should use the same words in the URL: drain-cleaning-services. Avoid stuffing irrelevant keywords or lengthy descriptions.
5. Use Schema Markup
A plumber SEO strategy isn’t complete without Schema markup. It is code added to your website that provides context about your content. It helps Google understand and show your content in search results.
You can use Schema to highlight key details people are looking for. This can be your business name, address, phone number, services, customer reviews, pricing, and areas.
By using relevant schemas (such as Local Business Schema, Service Schema, or Review Schema), you can show these details directly in the rich results. These will increase your visibility and encourage more people to click on your site.
6. Improve Website Speed
Website speed typically means how fast your webpages load when someone visits them. Why does it matter for SEO? The reason is that such sites offer a better user experience, which is a critical factor in Google rankings.
To improve your site’s speed:
- Compress images.
- Use browser caching.
- Minimize CSS and JavaScript files.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to distribute content faster.
- Test your site using Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix.
7. Use a Mobile-Friendly Design
A mobile-friendly design means your website should look and perform well on smartphones and tablets. Why? Google ranks mobile-optimized sites higher. And research by ReviewTrackers shows that 57% of people use mobile devices to find local businesses online.
To optimize for mobile devices:
- Use a responsive web layout that adapts to any screen size automatically.
- Keep buttons large and navigation simple.
- Analyze your website using a Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
8. Use HTTPS
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the connection between your website and its visitors. It helps keep sensitive data, such as contact forms and payment details, safe from hackers.
Search engines consider HTTPS a ranking factor because it indicates trust and security. You can enable it by purchasing and installing an SSL certificate from your hosting provider.
9. Build Quality Links
Backlinks are one of the most effective strategies in SEO for a plumbing company. These are links from other websites that direct back to your plumbing website. The higher quality these links are, the more trustworthy your site becomes in Google’s eyes.
By high quality, it means your backlinks:
- Come from authoritative, reputable websites
- Are contextually relevant to your content or industry
- Use natural, descriptive anchor text
- Come from diverse domains (not just one source)
- Are earned organically – not paid or spammy
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Plumber SEO
SEO marketing for plumbing companies can only be effective when done right. Here are four common mistakes to avoid:
- Keyword Stuffing: Overusing keywords can trigger Google’s spam detection and lower your ranking.
- Duplicate Content: Copying or rewording others’ work adds no unique value; Google favors original content.
- Outdated Content: Older or decaying content loses relevance as trends change. Regularly update them with fresh information.
- Lack of Multimedia: Users prefer visual content; include images, infographics, and videos to keep them engaged.
Final Words
When done right, SEO for plumbers helps your business stay ahead of competitors and grow steadily. Expert plumbing SEO services can make this process more effective. At PNC Logos, our team of SEO experts has helped many small businesses improve their website rankings and increase sales. We use tested methods tailored to your specific industry to deliver measurable results. If you want to stand out from the competition and grow your business, get in touch with us today!
Read more -
 October 28 2025
October 28 2025
How to Fight Content Fatigue and Keep Your Audience Engaged
If you’re publishing five posts a day and still seeing your engagement drop by 40% compared to last year, you’re likely facing content fatigue.
It’s true! Engagement rates across major platforms are dropping because of repetitive and low-value content.
In fact, Instagram’s engagement rate is down by 28% YoY (Social Insider).
But there’s a way out…
You can regain attention by creating fewer but higher-impact posts that feel fresh, emotional, and relevant.
In this guide, you’ll learn what content fatigue is, how to avoid it to drive meaningful engagements, and make your brand feel alive again.
What is Content Fatigue?
In Digital Marketing, content fatigue meaning encompasses a state of feeling overwhelmed or indifferent to online content, either because it provides no value or lacks originality. The key signs of content fatigue are a decrease in key engagement metrics. These include a reduced click-through rate, watch or read time, and fewer likes, comments, or shares compared to before.
These are not just numbers. These metrics mean that your audience is losing interest in your brand. As a result, it decreases your marketing ROI (return on investment). Also, content fatigue differs from content creation fatigue, which involves being overwhelmed by the pressure to produce more content consistently.
Why Does Content Fatigue Happen?
Think about it. Your target industry is full of brands vying to attract consumers and grow their business. The result? Your audience is constantly receiving the same information from multiple sources. If your content does not provide a unique value, they have no reason to stick around. This behavior has become even more noticeable recently. Here is why:

- Content Overload is real.
According to Exploding Topics, around 402.74 million terabytes of data are created every day. And a projected 181 zettabytes is generated in 2025 alone. The sheer volume of information bombarding people online is staggering.
- People are less attentive today.
Data from SQ Magazine indicates that the average human attention span has reduced to about 8.25 seconds. Moreover, according to Facebook, many mobile users spend only about 1.7 seconds deciding whether to engage with a piece of content.
- Engagement is dropping.
According to Rival IQ, engagement rates are dropping across all major platforms by double-digit percentages. Facebook is down 36%, Instagram 16%, TikTok 34%, and X 48%. This means that people are tuning out rather than interacting through clicks, likes, or shares.
- Time for consumption is not increasing. But content volume is.
A recent survey by Deloitte has found that people spend almost 6 hours per day on media and entertainment. And from 2024 to 2025, this hasn’t materially increased. However, more content and data are being created every day.
- Mental fatigue is here.
A 2024 meta-analysis on Information Overload found strong links between information overload, burnout, and reduced cognitive performance. As a result, this mental fatigue makes people more likely to skim past rather than engage deeply with content.
How to Avoid Content Fatigue: Key Strategies That Work
The answer is simple: don’t create more content. Create better content instead. Below you’ll find practical ways to achieve this by creating content that keeps your audience engaged.
1. Publish High-Value Content, But Less Frequently
Publishing high-value content means creating fewer pieces – but making each one worth your audience’s time. A case study by HubSpot found that posting up to 35 times per week brings only a negligible 5% increase in website traffic. This means that your audience can only consume so much in a given period of time.
Also, research by the Content Marketing Institute found that 83% of marketers differentiate themselves from competitors by creating better quality content. Meanwhile, only 30% achieve it by producing more. These numbers prove that volume alone no longer drives engagement. Quality does.
To create high-value content:
- Focus on your audience’s needs and search intent.
- Back up claims with credible stats, case studies, and quotes from experts.
- Provide in-depth value, not just surface-level, lengthy content.
- Keep your voice consistent with your brand’s values and tone.
- Cut unnecessary words tightly. Every sentence should serve a purpose.
2. Be Creative and Original
Another way to keep your audience engaged is by delivering information they haven’t seen or read before. You need to add a fresh perspective and a unique voice, instead of repeating what’s already out there. When people learn something new from your content, they will keep coming back for more. This can help you beat content consumption fatigue.
To stay creative and original:
- Instead of copying trends, reinterpret them from your own experience.
- Use data, insights, and stories to create a stronger impact.
- Check existing content and ensure yours adds fresh value.
- Share genuine experiences and lessons instead of polished marketing talk.
- Partner with creators, customers, or experts to bring in diverse viewpoints.
3. Create Interactive and Diverse Content
Interactive and diverse content goes beyond passive reading or watching. It invites your audience to participate. This can be through polls, quizzes, interactive videos, or user-generated content. This strategy engages people and makes them feel involved in your brand.
According to a study by Demand Metric, interactive content generates 2 times more conversions than passive content. Another factor that can help is connecting with your customers through diverse content formats. These include videos, blogs, infographics, podcasts, and more.
To create more interactive and diverse content:
- Add polls and quizzes.
- Create interactive videos.
- Offer challenges or competitions with rewards.
- Ask followers to share their stories and opinions.
- Align content recommendations to user behavior or preferences
4. Give Your Audience Memories, Not Materials
Today, consumers want meaningful experiences from brands, not just content. In fact, data from GWI suggests that 58% of Americans prefer spending money on experiences, which is 14% more than the global average.
One way to make your brand experience memorable and reduce consumer fatigue is to use emotional storytelling in your campaigns. In fact, research by Fast Company found that advertising campaigns with purely emotional content perform 2x as well as those with only rational content. When your message makes people feel emotions like joy, curiosity, or even empathy, they’re more likely to remember your brand and share it.
How to use emotional storytelling effectively:
- Start with purpose. Know the “why” behind your message.
- Show real people. Use relatable characters or customer experiences.
- Show how problems are felt, not just how they’re solved.
- Use visuals to portray the emotion. Choose imagery, colors, and words that fit the mood.
- Keep it authentic. Avoid exaggerated claims. Genuine stories build trust.
- End with meaning that inspires or motivates your audience.
5. Distribute Content Across Multiple Channels
Data from Statista shows that as of October 2025, 73.2 % (6.04 billion people) of the world population uses the internet. Of this, 68.7% use social media. Moreover, every social media user engages with an average of 6.83 different social media platforms, according to Backlinko.
What does this indicate? If you’re only posting on one platform, you miss out on countless other ways to engage your audience. It’s not about posting the same thing everywhere. It’s about adapting your content to fit each channel’s format and audience behavior.
How to do it effectively?
- Identify where your audience spends the most time.
- Tailor content format to their preferred channels
- Repurpose lengthy content into multiple short formats like a carousel, infographic, video clip, or email.
- Plan and automate posts to stay consistent without overloading followers.
- Monitor engagement by platform and focus on what drives the most interaction.
6. Make Your Content Feel Personal
One major cause of content consumption fatigue is irrelevant and generic content. The solution? Content personalization. It is a powerful strategy to make your audience feel heard and valued. And no, it’s not just about using their name in newsletters or messages. You need to understand their problems, how they prefer to solve them, and the right time to deliver the right message.
How does this help fight content fatigue? Data from Blogging Wizard shows that 76% of consumers get tired of businesses that do not offer personalized experiences. Moreover, Optimove’s Consumer Marketing Report shows that 81% of consumers are more likely to open an email tailored to their interests than one that simply uses their name.
Practical tips to personalize your content:
- Group users by interests, behavior, or stage in the buyer journey.
- Analyze engagement metrics to understand what topics or formats work best.
- Create solutions that address your audience’s specific pain points.
- Match your language and style to your audience’s preferences.
- Use AI for content recommendations, personalized emails, or predictive insights.
- Reply to questions and provide feedback to strengthen the connection.
7. Refresh Old and Decaying Content
Content decay means a gradual decrease in a piece of content’s organic performance and visibility in search results. What does it mean for content marketing fatigue? No matter how much value you pack into your content. Over time, the information becomes outdated, as new trends emerge and facts change.
The result is a large piece of irrelevant content that fails to deliver any real value to the reader. Refreshing it with updated content keeps your best-performing pieces relevant and timely for your audience.
To refresh content effectively:
- Audit your content library: Identify outdated and low-performing pieces.
- Update information: Refresh statistics, links, and examples with the latest data.
- Boost SEO: Add relevant keywords, meta descriptions, and internal links.
- Enhance visuals: Use new images, charts, or infographics to improve clarity.
- Repurpose content: Convert posts into videos, infographics, or social media
- Align with user intent: Address the current audience’s needs and search behavior.
- Re-promote it: Share content across all channels to increase reach and visibility.
8. Get Feedback from Your Audience
Metrics may tell you about the lack of engagement with your content. But listening to your audience helps you understand the reasons behind the consumer fatigue. By getting feedback, you get a clear understanding of what they like, what they skip, and what they want more of.
It also helps build trust and keep your audience engaged. In fact, data from Forbes suggests that 77% of people view brands more favorably if they gather and apply customer feedback.
How to gather and use feedback effectively?
- Run quick polls or surveys on social media or via email marketing.
- Ask what topics or formats they prefer.
- Encourage honest responses through open questions.
- Listen to what people say about your brand or niche on online forums or social sites.
- Create feedback loops to keep your content fresh and relevant.
Other Types of Content-Related Fatigue You Should Know
Content fatigue can take many forms besides just consuming content. It can affect both audiences and creators. Here are some other types to spot early and tailor your strategies to stay engaging.
- Content Creator Fatigue: Exhaustion from producing content non-stop. It includes algorithm pressure and a lack of creative breaks.
- Marketing Fatigue: Also called brand fatigue, it happens when consumers tune out repetitive or irrelevant ads, emails, and brand promotions.
- AI Content Fatigue: Overuse of AI-generated content that is generic and emotionless. It feels less personal and leads to lower engagement.
- Social Media Content Fatigue: Your followers are seeing too many posts from different brands with the same message – multiple times a day.
Final Words
Content fatigue is costing brands not only traffic but also meaningful engagement. To overcome it, focus on creating high-value and audience-centric content. Build connection through immersive experiences and memorable content. Refresh old content and align your content strategy around your audience’s pain points.
At PNC Logos, we help businesses like yours with research-backed digital marketing strategies. We know that you want to increase your online presence and keep customers coming back. So, we do the heavy lifting to get you there. Contact us today to fight content fatigue and grow your business.
Read more -
 October 23 2025
October 23 2025
SEO for Painting Contractors: How to Rank Higher & Get More Projects
According to BrightLocal, 66% of people trust Google to research local businesses online, and 36% prefer going directly to a company’s website.
Now let’s see how this works for painting contractors. If you’re not showing up in these searches, you’re not just missing traffic. You’re missing out on opportunities to book more projects. And while you’re invisible, your competitors are scooping up those high-quality leads.
The solution? SEO for painting contractors. With the right SEO strategy, you can rank higher on search results, attract leads that actually convert, and ultimately grow your painting business.
This guide explains the best SEO strategies for painters to show up on Google’s No. 1 page and win more painting jobs!
What is SEO for Painters?
SEO for painters is a strategic process of making your painting business rank higher in searches on Google and other search engines. The goal is to make your website appear near the top on the first page of search results whenever a customer searches for services like yours.
Typically, SEO for painting companies includes the following strategies:
- Local SEO: Appear in nearby searches with maps and reviews.
- On-page SEO: Optimize website pages with keywords and clear content.
- Off-page SEO: Gain authority through backlinks and online mentions.
- Technical SEO: Improve site speed, mobile use, and structure.
- Modern Trends in SEO: Adapt to voice search, AI, and Google updates.
Let’s review each in detail in the following sections.
Local SEO for Painting Contractors
Local SEO helps your site show up when people in your area search for services like “house painter near me” or “painting contractor in (your city)”. So, if your business is located in Orlando, and someone types “exterior house painter Orlando” into Google, a strong local SEO ensures you appear in the top three local listings as well as in organic results.
Key strategies in local SEO for painters include the following.

1. Optimize Google Business Profile
Google Business Profile (GBP) is a free tool from Google that includes comprehensive details about your local painting business. It is your business listing that shows up on Google Maps and local search results.
Why does it matter? Research by SOCI shows that 50% of American consumers aged 25-34 rely on Google Maps to find local businesses. And according to Google, people are 70% more likely to visit and 50% likely to purchase from companies with a complete Business Profile.
To optimize your Google Business Profile:
- Claim & verify your Google Business Profile on Google’s business site.
- Select categories. Use “Painter,” “House Painter,” or “Painting Contractor” as your main category.
- Complete all fields. Services, service areas, hours, website, and phone.
- Add quality photos. Before/after projects, team shots, or branded vehicles.
- Post weekly. Share promotions, offers, or recent work.
2. Include Local Keywords
Local keywords are basically the search terms that connect your service to a specific location. Why is it important? Data from Backlinko shows that 46% of searches on Google have a local intent. The idea is simple. You want to show up when people nearby are actively searching for painting services.
But, how do you find these keywords? Free platforms like Google Keyword Planner are a great place to start. You can also utilize expert painter SEO services that understand your industry standards. A common approach is to take your primary keyword and pair it with the name of the city or region you serve. For example, if your main keyword is “interior painting” and you’re targeting Florida, you’d go with “interior painting in Florida.”
3. Reviews and Testimonials
Written feedback doesn’t just influence buyers. It also shapes how Google views your business. In fact, a survey from local SEO experts shows that High Numerical Google Ratings, like 4-5, is the 6th most influential local pack/finder ranking factor. Google pays close attention to the authenticity, quality, and frequency of reviews. That’s how it decides whether your business deserves a higher spot in local search results.
To optimize reviews in SEO for house painters:
- Use follow-up emails to request reviews. Offer perks like discounts or loyalty points as incentives.
- Acknowledge positive reviews to build goodwill and repeat business.
- Respond promptly to negative reviews with solutions. Show commitment to customer care.
- Showcase great feedback on your website and social media to strengthen brand credibility.
4. Directories and Citations
Directories are online places where your business is listed, such as Angi, Yelp, or Houzz. Think of them like modern-day phone books on the internet. These listings make it easier for people to find and mention your business online (called citations).
Winning citations are a critical component in SEO for a painting company. The more often Google sees your painting business listed in trusted places, the more confident it is that your company is reliable. As a result, your site gathers more authority and ranks higher in search results.
5. NAP Consistency
NAP is the shorthand for your company’s name, address, and phone number. SEO for painters and decorators requires that these elements remain the same across all online mentions and listings of your business. Why? Consistent NAP tells Google that the information it has on your business is correct and reliable enough to show in search results. Meanwhile, inconsistent NAP details can confuse customers and suggest that your business is not trustworthy.
On-Page SEO: Improving Your Website to Rank Higher
On-page SEO is the next step in any painter and decorator SEO strategy. It focuses on improving the pages of your website so that Google understands exactly what services you offer. Unlike local SEO, these strategies expand beyond regional searches to target broader search terms and user intents.
When optimizing on-page elements, you need to focus on the following factors.

1. Keyword Research
Keywords are the exact phrases your ideal customers type into Google when they’re looking for painting contractors. Google uses those keywords to decide whether your page should show up in search results. When looking for keywords, consider:
- High search volume
- Low keyword competition
- Primary keyword (describes your business’s overall niche)
- Secondary keywords (semantic terms, supporting the primary keyword)
- Long-tail keywords (descriptive phrases or questions with a specific intent)
2. Optimizing Content
Once you have your search terms, it’s time to create content around them. Start by creating content for your service pages. The aim is to help Google and people know what your page is about so it can rank for searches.
Blogs are also a powerful way to target broader search intents with more comprehensive information. You can create content for blogs using long-tail keywords. For example, if people are searching “How often should you repaint a house exterior?”, you can write a post breaking it down by climate, materials, and paint quality. This kind of comprehensive content gives you more credibility and portrays you as the go-to expert in the industry.
When creating content using SEO for painting contractors:
- Add your primary keyword naturally in the main headings and body content.
- Use Header Tags like H1 > H2 > H3 to make your content easy to crawl.
- Link to related pages of your site. Use descriptive anchor text to provide content.
- Give your images a keyword-rich description so Google understands what it’s about.
Calls-to-Action (CTAs)
Calls to action are simple prompts that guide people to take the next step, whether that’s using your service or buying your product. Include a clear CTA in every section of your service pages. Make it specific, straightforward, and easy to click.
Phrases like “Take your home interior to the next level” may sound fancy, but they don’t really tell what the user needs to do. Instead, you can say to “Get a Quote,” “Sign up,” or “Book a Painting Consultation.” And avoid over-the-top, salesy language. Keeping your CTAs professional helps build trust in your brand.
Off-Page SEO: Get Other Sites to Recommend You
Off-page SEO means all actions you take beyond your website in an effort to increase your search rankings. Some core activities include earning backlinks, driving branded searches, and increasing engagement on social platforms.
1. Earn High-Quality Backlinks
Backlinks are a link-building strategy where other websites use links in their content to point back to yours. The more trusted and relevant those websites are, the better. You can earn these by writing guest articles, creating helpful content that others want to share, or reaching out when you see a broken link and suggesting your content as a replacement.
2. Take Advantage of Social Signals
Social media likes, shares, and comments don’t directly affect your Google ranking, but they spread your content to more people. The more visibility you get, the higher the chance that others will mention your brand or link to your site later.
3. Boost Your E-E-A-T
EEAT stands for Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust. This is Google’s way of measuring how trustworthy you look online. To build it, get your brand or team mentioned on credible sites. You can also collect positive reviews and show proof that you know what you’re talking about.
4. Drive Branded Searches
Encourage people to search for your brand name directly on Google. This tells Google that people are looking for you specifically. Campaigns, videos, or content that make your brand memorable can help you drive this type of search behavior.
Technical SEO: Improve Your Site’s Page Experience
Technical SEO involves improving your site’s technical aspects such as design, speed, navigation, and security. It aims to help search engines find information and index your website. It also provides a seamless experience to users so they stay on your site and take action.
Here’s how technical SEO works.
1. Optimize for Mobiles
Data from Global Stats shows that 59.1% of internet traffic comes from mobile devices. As a result, Google has adopted a mobile-first indexing approach. This means it prefers how well the mobile version of your site works to decide whether to rank it in search results. Moreover, most people use mobile devices to search for information online. Therefore, optimizing your painting website for mobiles is non-negotiable.
2. Improve Your Page Speed
Research from Portent shows that a webpage that loads in 1 second has a 3 times higher conversion rate than one that takes 5 seconds. Speed is also part of Core Web Vitals, which are factors in Google’s “page experience” ranking signals.
To optimize loading speed:
- Compress large images on your site. They take less time to load.
- Use a CDN or content distribution network. Connects users to the nearest server or copies of webpages so they take less time to load.
- Minify JavaScript, CSS, and HTML files. Removes whitespace and reduces file sizes.
Keeping Up with Modern SEO and New Search Trends
Search engines are getting more intelligent with the continuous updates and the introduction of AI. Knowing how the trends are shifting can help you adjust your modern SEO strategies and stay visible in online searches. Here’s what to do.
1. Optimize for AI Searches
From Google’s AI Overviews and AI Mode to ChatGPT and DeepSeek, AI search algorithms are changing how your customers find your business and visit your website. Optimizing your content to these searches can help you show up right where your customers are.
To optimize for AI searches:
- Focus on semantic search or the context behind the query rather than keywords.
- Include schema markup to help AI understand what you’re writing.
- Use a natural conversational tone that AI systems can understand easily.
- Create first-party content around Google’s E-E-A-T standards.
2. Create Video and Interactive Content
Video and interactive formats can drive engagement and ROI far more than text alone. Data from Wyzowl shows that video marketing gives 93% marketers a positive ROI. Invest in short and personalized video prospecting. Use video to demonstrate your products or services.
3. Adapt to Voice Searches
Voice searches are about natural and conversational queries. Why does it matter? Because 35% of U.S. households now own a smart speaker. It is shaping how customers discover and interact with businesses.
To optimize for voice searches:
- Focus on long-tail keywords and conversational writing style.
- Use FAQs that match how a customer would speak about it.
- Ensure local SEO is strong for “near me” searches.
Final Words
If you want to land more painting projects, you need to show up in Google’s top search results by utilizing SEO for painting contractors. It’s because your customers are searching for painting services online. The best way to get the most bang for your efforts is to utilize expert SEO services for painters.
At PNC Logos, our team of SEO experts understands the nitty-gritty of your painting industry needs and target customers. If you want to gather more traffic and land more painting jobs, contact us now to get started
Read more -
 October 15 2025
October 15 2025
SEO for HVAC Companies: 10 Tips You Need to Get More Leads Online
Your HVAC business is great at fixing heating and cooling problems—but can customers find you online?
Most of your potential customers start their search on the internet. According to Invoca, 84% of people seeking HVAC repair call after conducting an online search.
This means if your business isn’t showing up on Google, you’re losing valuable leads to competitors who are. But how can you stand out against larger companies dominating the search results?
The answer is SEO for HVAC.
This guide offers proven HVAC SEO strategies to help your business rank higher in Google and turn online searches into real service calls.
What is SEO for HVAC Businesses?
SEO for HVAC contractors means improving your website and its content so it shows up higher on Google when people search for heating, ventilation, or air conditioning services online.
By ranking higher, essentially, it means showing up in the top organic (not paid) results. These results can include webpage links, featured snippets, AI Overviews, and the People Also Ask section. It might sound simple. But achieving these top positions requires a well-structured SEO strategy with carefully planned steps.
10 HVAC SEO Strategies to Attract More Customers
Below are 10 proven strategies to optimize your HVAC website and improve your organic search rankings. Let’s go through them one by one.
1. Local SEO for HVAC Contractors
Local SEO for HVAC companies involves strategies that focus on ranking your website in local search results. If someone searches for an “AC repair near me,” Google identifies nearby businesses that best match the query. If your HVAC company is properly optimized for local SEO, your website will appear among the top results in that area. For HVAC contractors, local SEO is non-negotiable, as most of these businesses serve specific cities or regions.
Local SEO tips for HVAC contractors include:

Google Business Profile
Google Business Profile is your company’s free listing on Google Maps. It is an integral factor in helping you rank in the Google Local Pack (the top three search results on Maps)
Data from Google shows that 76% of people who search for “near me” visit the business within a day. This means a well-optimized profile can directly increase your customer visits and give you an edge over competitors.
You can use professional HVAC SEO services that specialize in optimizing local listings to make this process easier. But if you want to do it yourself, here’s what to do:
- Claim and verify your Google Business Profile.
- Use exact details of your business name, address, and phone number.
- Add service areas and operating hours.
- Post updates and special offers regularly.
- Include high-quality photos of your office building, team, and work.
Schema Markup
Schema markup is a special type of structured data added to your website’s code to help search engines clearly understand your business details. These can be your services, location, contact information, and ratings.
HVAC company local SEO services can strategically use schemas to make your business’s key details directly visible in the search results. This makes it easier for people to know and trust your company.
Geo-targeted Content
Geo-targeted content is an integral part of HVAC SEO marketing. It involves creating web pages and digital marketing materials focused on specific locations where your HVAC company offers services. This makes it easier for search engines to connect your business with customers looking for HVAC services in their specific area. To make effective geo-targeted content:
- Create city or neighborhood-specific service pages
- Use local keywords naturally in titles, headings, and meta descriptions
- Add embedded Google Maps to your location pages
- Mention local landmarks or regions in your content
Reviews and Testimonials
Customer feedback plays a huge role in HVAC local SEO. Positive reviews and testimonials make your business seem more credible. In fact, a 2024 study conducted by BNP Media and ACHR News found that 91% of homeowners rely on online reviews when choosing a contractor.
Moreover, a recent survey by PickHvac shows that 37.5% of people use Google to check reviews of local contractors compared to other sites. Google also considers reviews when ranking businesses in local searches.
Some tips for managing customer feedback:
- Ask happy customers to give a Google review after each service call.
- Respond politely and promptly to both positive and negative feedback.
- Showcase strong testimonials on your homepage and service pages.
Online Citations
Online citations in HVAC search engine marketing mean the mentions of your business Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) across websites and directories. These mentions help Google verify that your business is legitimate and trustworthy. To optimize for online citations, you can:
- List your business in reputable directories like Yelp, Bing Places, Yellow Pages, Angi, etc.
- Use the exact same NAP details across all listings.
- Include a link to your website wherever possible.
- Update outdated listings to prevent confusion.
2. Make Your Site Easy to Navigate
Local HVAC search engine optimization helps you show up in local results. However, once visitors arrive, a well-optimized website is what keeps them engaged. If your website navigation is complex or designed poorly, visitors will leave quickly. This is known as the bounce rate.
A high bounce rate signals to Google that your website isn’t offering value to visitors. Over time, this can cause your rankings to drop in search results. To prevent this, your website should encourage visitors to stay longer and explore multiple pages.
Expert SEO services for HVAC companies can help you avoid high bounce rates by improving your site structure and optimizing user experience. This typically includes:
- Using a clear and organized menu with simple labels.
- Showing contact details at the top of the service page.
- Adding a search feature so people can quickly find specific information.
- Placing CTAs in each section (below the main header and all subheadings)
- Linking to key services pages from the homepage
3. Ensure Faster Loading Time
Page speed is another key factor in HVAC contractor SEO. It’s one of Google’s Core Web Vitals, which analyzes how well your website performs for users. Google uses these to evaluate user experience – a major ranking factor in search results.
It also encourages people to stay on your site and use your services. According to a study by Portent, a webpage that loads in 1 second has a 2.5 times higher conversion rate than a page that takes 5 seconds to load.
HVAC company SEO helps you reduce page loading time by:
- Compressing images and large files on your site.
- Minimizing HTTP requests by simplifying your page design.
- Enabling browser caching so returning visitors can load pages faster.
- Using a CDN (Content Delivery Network) to deliver content from servers closest to users.
- Testing your speed regularly using Google PageSpeed Insights.
4. Optimize for Mobile Devices
When improving your website for SEO, you have to make sure it is optimized for mobile devices. Why? Because Google now prioritizes the mobile version of a site to decide whether to rank it on its first page or not.
The reason is simple. A study by Data Reportal shows that 96.5% of users worldwide access the internet via their mobile devices. Therefore, your site should be easy to view and adapt to mobile screens to retain traffic and rank higher in Google search results.
5. Do Your Keyword Research
A fast and user-friendly website can only rank if it contains the right words your customers are searching for. That’s why the best SEO for HVAC contractors isn’t complete without keyword research.
Keywords are the specific terms and phrases people use when looking for HVAC services online. Using these keywords strategically across your website tells search engines what your business offers and to rank your pages for relevant searches.
Not all keywords are the same, however. Some types include:
- Primary keywords that represent your core offerings or services. For example, “HVAC maintenance/repair” or “HVAC installation.”
- Secondary keywords are related terms or phrases that support your primary keyword.
- Semantically related keywords (also known as LSI keywords) are words or phrases linked to a main topic that help search engines understand its context and relevance.
- Long-tail keywords are more descriptive and specific. These can be questions or phrases, such as “Types of residential heating and cooling systems.”
The following infographic provides more details on keyword types:

If you’re an HVAC company just getting started online, it’s best to start with SEO basics for HVAC companies. This means using less competitive long-tail keywords. But make sure they still have a good search volume.
You can find your keywords for free using Google search features. These can be Google Autocomplete, People Also Ask sections, and Related Searches. Otherwise, you can use dedicated tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMRush, Ahrefs, or Moz.
Once you have your keywords:
- Use them across your site’s headers, body content, and image alt texts.
- Avoid keyword stuffing. Keep your language natural and helpful.
- Create individual webpages (around relevant keywords) if you’re offering multiple services.
6. Create Quality Content
Content is a critical part of SEO marketing for HVAC contractors. Create valuable and engaging content around your keywords. The goal is to satisfy the questions your audience has and provide helpful solutions that build trust.
The better you create content aligned with user intent, the higher it can rank in search results and attract more customers.
Types of content you can create include:
Service Pages:
These include content that specifies the services you offer. Create one page per service to connect with the right customers. Include local keywords and clear calls to action, such as “Schedule Service” or “Get a Free Quote,” to drive conversions.
Blogs:
Blog posts help you target informational and long-tail keywords while building authority in your field. When creating blogs:
- Focus on customer pain points. For example, “Why is my air conditioner leaking water inside?”
- Provide solutions with comprehensive information to satisfy the search intent.
- Structure content into short paragraphs and headings (H1, H2, H3) for readability.
Images and Videos:
Visual content makes your HVAC website more engaging and trustworthy. A study by video hosting service Wistia found that people spend about 1.4 times more time on pages with video than those without. Google also uses image and video optimization as part of its ranking signals.
7. Meta Descriptions And Page Titles
When your website ranks for a search query, the first thing people see is the page’s title and a short description. These can shape your first impression and determine whether a searcher will visit your page. To make them effective:
- Include your primary keyword and location.
- Clearly state what the page offers.
- Keep titles under 60 characters.
- Write descriptions under 160 characters.
- Use a clear and action-oriented tone that encourages clicks.
8. Use Internal Links
Internal links are another critical factor in on-site SEO for HVAC. These connect one page of your website to another, so both people and search engines can navigate your site easily. Internal links can also distribute authority from one page to others and strengthen your site’s overall authority.
When adding internal links, use descriptive anchor text to provide more context. Also, link to relevant pages, such as service areas and blogs, to strengthen SEO and keep visitors engaged.
9. Gain Quality Backlinks
Creating backlinks is a powerful link-building strategy that involves getting other websites to direct links back to yours. In SEO for an HVAC company, your backlinks should come from reputable sources. These can be local directories, partner businesses, and industry blogs.
But how do you earn these? The best place to start is creating valuable, original content that encourages shares across other websites. You can also guest post or ask your connections to link to your content. But make sure they are relevant to your industry.
In the words of SEO expert Brian Dean himself:
“You really only want to get links from relevant websites. If it’s not relevant, it’s not going to have much of an impact. Plus, these people might be (rightly) hesitant to link to your jewelry store from their football blog.”
10. Stay Informed About the Emerging Trends
SEO tactics are constantly evolving thanks to algorithm updates and new search technologies. So, make sure to stay updated on the modern SEO trends to adapt your strategies on time and get ahead in the competition.
To stay visible, align your HVAC SEO strategy to the following emerging trends:
- Search Intent over Keywords: Instead of only keywords, Google now considers search intent for ranking. Your content should address the intent of the target keyword with comprehensive, in-depth, and relevant information.
- AI Search Engines: These include Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and AI tools such as ChatGPT and DeepSeek. To optimize for these, focus on semantic searches, long-tail keywords, and structured content.
- Voice Searches: More homeowners are using voice assistants like Alexa or Google to find services online. To adapt to these searches, your content should use a natural and conversational tone. Also, include FAQs that match spoken questions.
Final Words
Today, your ideal customers are searching online. SEO for HVAC companies helps you attract these customers, land more projects, and grow your business. But these strategies can only be most effective when done right.
At PNC Logos, our team of HVAC SEO experts deeply understands the complexities of modern search engines. We use proven strategies to help your business get more online traffic and drive meaningful conversions. If you’re ready to build a stronger online presence, get in touch today!
Read more
Get In Touch
Get In Touch




